Health Capsule
Protect Your Hearing
Loud sounds can harm tiny structures in your inner ear. This can lead to noise-induced hearing loss or a condition called tinnitus. Tinnitus can cause buzzing, hissing, or humming in your ears. Hearing loss can happen instantly, or gradually over time. The louder the sound, the more damage it can cause.
You can protect your hearing by moving away from loud sounds or turning down the volume. You can also use hearing protectors, such as earplugs or protective earmuffs.
Consider using hearing protectors if you know you’ll be in a loud setting, like concerts, sporting events, or firework displays. Hearing protectors can also help in noisy workplaces or when operating loud machinery, like lawn mowers and drills.
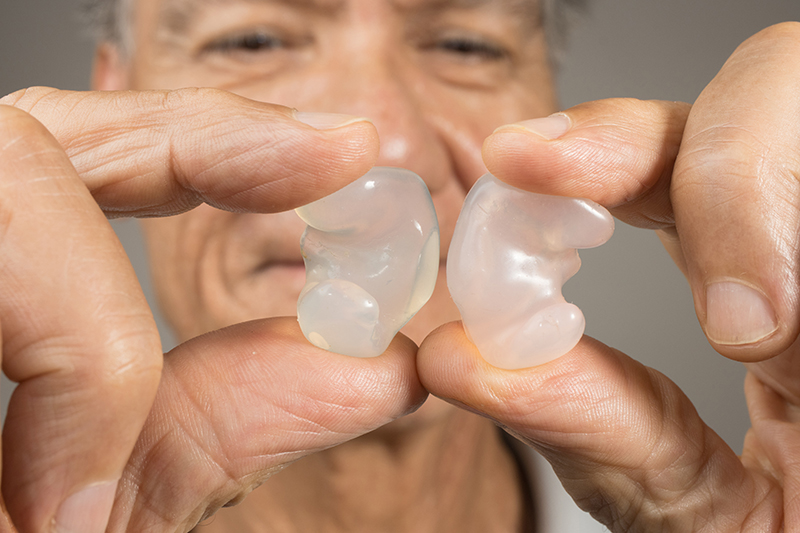
There are different types of hearing protectors. Choose a type that’s comfortable and easy for you to use. Most earplugs are inexpensive. Some are made of soft foam. Others, called pre-molded earplugs, can be made of plastic, rubber, or silicone. One type, called pre-molded high-fidelity earplugs, can be helpful at movies or concerts. They protect hearing without reducing sound quality.
Protective earmuffs are another option. They reduce noise by completely covering both ears. They look like headphones. But earmuffs might not work as well for people who wear glasses, which can create gaps that make the fit less tight. Learn more about hearing protectors.
NIH Office of Communications and Public Liaison
Health and Science Publications Branch
Building 31, Room 5B52
Bethesda, MD 20892-2094
Contact Us:
nihnewsinhealth@od.nih.gov
Phone: 301-451-8224
Share Our Materials: Reprint our articles and illustrations in your own publication. Our material is not copyrighted. Please acknowledge NIH News in Health as the source and send us a copy.
For more consumer health news and information, visit health.nih.gov.
For wellness toolkits, visit www.nih.gov/wellnesstoolkits.




